BANGKOK, Thailand, Jan 23 (IPS) – Asia and the Pacific is house to 54 per cent of the world’s city inhabitants, who’re disproportionately susceptible to the impacts of local weather change (ESCAP, 2023; IPCC, 2022). Why then, do local weather motion tasks in cities generally face delays in implementation?
Essential new developments in mitigation and adaptation together with: renewable power, public transport, and nature-based options, are wanted to safeguard the lives of billions, but many battle to safe adequate funding. The truth is, research estimate that, globally, there’s a $6-$12 trillion hole in annual funding for local weather and resilience funding (Buchner and others, 2023).
Of the funding that does are available in, solely 10 per cent goes to adaptation tasks (Negreiros and others, 2021), highlighting an actual want to deal with human vulnerability in cities. So how can cities draw from larger sources of personal and public investments for local weather motion?
Maybe one answer is matchmaking – however not the sort you’re considering of.
Urban-Act is a global venture funded by the Authorities of Germany’s Worldwide Local weather Initiative (IKI) with ESCAP as an implementing companion that seeks to speed up entry to city local weather finance. City-Act facilitates venture preparation for cities, serving to transfer their tasks alongside the city local weather finance worth chain to allow them to appeal to public or personal finance.
That is adopted by metropolis local weather finance matchmaking, the place cities are related with potential traders via in-person occasions or on-line platforms. This course of is explored intimately in ESCAP’s 2023 working paper, Enabling Innovative Investments.
The paper highlights how venture preparation and matchmaking can unlock the potential of public-private partnerships (PPPs) to bridge the local weather finance hole and speed up local weather motion in cities. Nevertheless, a number of challenges have to be addressed.
These challenges embrace:
- • Inadequate venture preparation: cities usually lack the capability and sources to organize ‘bankable’ local weather tasks that traders are keen to fund.
• Restricted reporting on success: only a few matchmaking programmes report on the success charges of the tasks they fund, making it onerous to judge and enhance matchmaking help.
• Restricted replicability and scalability of interventions: as cities all range of their ranges of improvement, political and financial programs, and native geographies, the help they require varies too, which will be onerous to duplicate elsewhere.
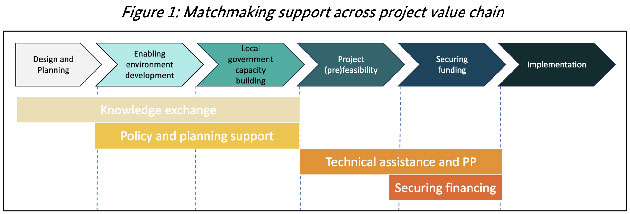
The identical paper highlights some potential options for offering cities with more practical help. As traders usually keep away from local weather tasks because of massive upfront prices and better perceived dangers, cities can search blended finance between personal and public traders, utilizing public grant cash to organize well-developed tasks, making them enticing to personal traders because of smaller ticket sizes (the quantity of capital for every share) who can then fund later stage implementation (see determine 1 to visualise venture worth chain).

One other answer entails monetary aggregation. Right here matchmaking programmes can take into account working with a number of cities with related tasks to raised replicate interventions, and/or they might compile many small tasks from one metropolis into one portfolio, rising funding as they leverage of economies of scale and diminished transaction prices.
Enabling Innovative Investments (2023) lists a collection of suggestions for efficiently using these options and in the end enabling efficient metropolis matchmaking. They vary from encouraging affect assessments for studying from errors to partaking in investor session early to align tasks with investor standards.
• To attain blended financing:
- o Have interaction in personal investor session at early levels of venture design
o Guarantee tasks are aligned with nationwide methods.
o Make use of on-line platforms equivalent to CDP Matchmaker, SOURCE, or CI Portal.
• Whereas
- o Offering lists of project-types they’re fascinated with funding over the subsequent 12-18 months.
• To valorize monetary aggregation:
- o Take into account a ‘metropolis cluster strategy’ to extend replicability of interventions
o Enhance scalability by compiling a number of metropolis tasks into one portfolio.
• To enhance the effectiveness of matchmaking efforts in the long run:
- o Promote capability constructing to equip native governments with the experience and management for implementing tasks and securing personal finance
o Undertake an affect evaluation framework for monitoring and analysis to tailor programmes for optimum effectiveness
Regardless of the uneven break up of funds that goes in direction of mitigation tasks, present traits present we’re straying away from the 1.5°C warming goal globally agreed upon on the Paris Settlement in 2015, emphasizing simply how essential it’s that we speed up local weather finance in cities, significantly for adapting to the antagonistic results of local weather change which are anticipated to extend with time.
Tasks equivalent to City-Act that make use of venture preparation help and metropolis matchmaking, together with the suggestions developed within the Enabling Innovative Investments (2023) paper, may help bridge the numerous funding hole for local weather motion, making approach for extra sustainable and local weather resilient cities.
Liam O Connor, is Intern, Atmosphere and Growth Division, ESCAP; Francisco Martes Porto Macedo is Senior Program Affiliate, Cities Local weather Finance Management Alliance, Local weather Coverage Initiative; Omar Siddique is Financial Affairs Officer, ESCAP.
IPS UN Bureau
Follow @IPSNewsUNBureau
Follow IPS News UN Bureau on Instagram
© Inter Press Service (2024) — All Rights ReservedOriginal source: Inter Press Service




