
WASHINGTON DC, Jan 31 (IPS) – Nations within the Asia-Pacific area face a shortfall of a minimum of $800 billion in local weather financing. With public funds depleted by the pandemic, policymakers should unlock the huge potential of personal capital to hitch the combat extra successfully in opposition to world warming.
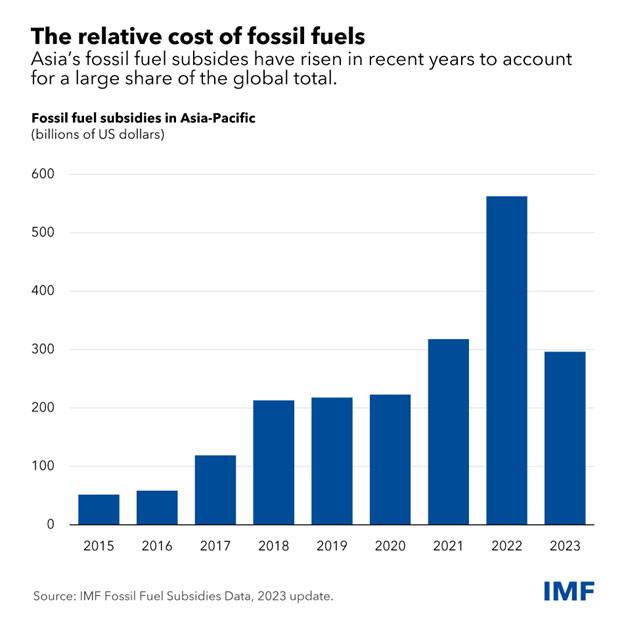
Doing so will demand a coordinated and multi-faceted strategy by actors on all sides, from governments and central banks to monetary supervisors and multilateral establishments. Necessary methods embrace phasing out fossil-fuel subsidies, which have reached a report $1.3 trillion. It’ll even be key to develop carbon pricing, bridge crucial data gaps, and promote modern financing together with public-private partnerships.
Asia-Pacific international locations skilled, on common, six pure disasters a 12 months over the previous three many years – about twice as many as growing international locations of Latin America and the Caribbean and about thrice as many as in sub-Saharan Africa.
Here is an explainer primarily based on our latest research, which pulls on current chapters of the World Monetary Stability Report on scaling up climate finance and different IMF studies on climate issues:
- Why is local weather finance pressing? Progress is simply too gradual. World temperatures are set to surpass the crucial 1.5 levels Celsius threshold above pre-industrial ranges. Efforts to halve 2019 ranges of greenhouse gasoline emissions by 2030 fall alarmingly quick, focusing on solely an 11 % discount. With out stronger motion, our warming planet imperils properties, well being, and meals safety. Mobilizing extra local weather finance is important not just for mitigating emissions however to construct adaptive capability by means of investments in local weather resilient infrastructure. That is particularly vital for Asia, which is house to a number of of the biggest emitters and a area acutely susceptible to local weather change as a consequence of excessive inhabitants density and geography.
- What makes Asia’s function pivotal? The area’s transition to larger sustainability has world implications. Asia contributed about two-thirds of world progress final 12 months, and can once more in 2024, however its heavy reliance on burning coal for power signifies that it contributes greater than half of dangerous world greenhouse gasoline emissions. Asia’s economies acknowledge how local weather hazards straight influence lives and livelihoods, and have made deeper commitments, as their revised Nationally Decided Contributions beneath the 2015 Paris Settlement present. Asia can help the local weather combat by demonstrating how one can stability financial progress and environmental sustainability.
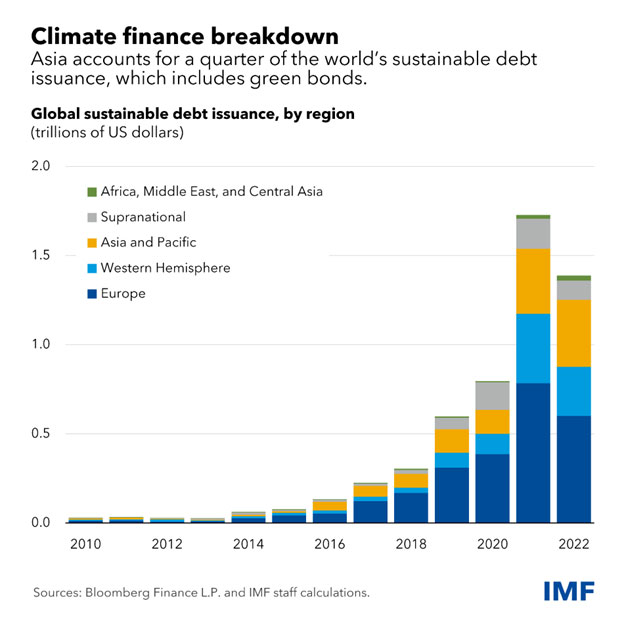
- How vital is the funding hole? Asia’s rising market and growing economies want funding of a minimum of $1.1 trillion yearly to satisfy mitigation and adaptation wants. However they’re solely getting $333 billion, largely from sustainable debt devices like inexperienced bonds, and public sources contribute greater than half. Such a shortfall leaves these economies with a funding hole of a minimum of $815 billion. China leads in attracting local weather finance, making main strides in renewable power adoption, and its collaborations with the EU have yielded essential frameworks for sustainable finance, such because the Widespread Floor Taxonomy and stricter China Inexperienced Bond Rules.
- What are the largest challenges? Pacific island international locations and different small economies typically have hassle accessing worldwide capital markets or acquiring financing by way of world local weather funds. Specifically, they discover it laborious to satisfy stringent accreditation necessities of world local weather funds as their capability is already stretched skinny and public funding administration is difficult. For bigger international locations, inexperienced bonds could also be as pricey as typical securities as a result of buyers look like much less trusting of inexperienced traits in Asia’s sustainable debt devices. These points underscore the broader challenges for the area’s funding aspirations.
- What do international locations say? A survey of 19 international locations in Asia revealed vital gaps in information, disclosures, and taxonomies, and that these are exacerbated by inconsistent nationwide local weather insurance policies that may promote fossil gas subsidies. These deficiencies undermine investor confidence in forward-looking targets and transition. Greenwashing is also a threat, respondents say, as a result of it might name into query the legitimacy of environmental claims made by bond issuers. As well as, growing geoeconomic fragmentation, together with friend-shoring and fraying world provide chains, might threaten cooperative and collective motion to include local weather change.
Motion to unlock far more local weather finance requires coordination amongst businesses overseeing local weather initiatives, plus collaboration between native and world entities:
- How can Asia’s governments assist? A method can be to comprehensively improve the framework on information, taxonomies, and disclosures. They need to section out fossil gas subsidies and develop carbon pricing, which might generate income for sustainable public funding. This may assist increase funding in inexperienced expertise, jobs, and progress, whereas supporting susceptible households. Measures that strengthen macroeconomic and public funding administration will assist scale back threat premiums and funding prices, drive financial progress, and entice personal capital.
- The place do central banks and monetary supervisors slot in? They need to promote world requirements for clear and constant disclosures, whereas strengthening local weather threat analyses and incorporating climate-related monetary dangers into prudential frameworks to reinforce monetary stability. Lastly, collaborating with multilateral commonplace setters to develop inner capability is essential for enhancing the readability and reliability of ESG rating rankings, fostering larger belief and understanding in these evaluations.
- What’s the IMF’s function? The Fund is working with member international locations to higher element climate-related financial dangers and insurance policies in surveillance and lending actions. The IMF is also strengthening information and statistics, together with by means of capability constructing and peer studying, to develop frequent requirements for measuring and analyzing local weather threat.
- Lastly, our Resilience and Sustainability Trust will help susceptible low- and middle-income international locations catalyze financing from different sources by restoring sound macroeconomic administration and constructing the institutional capability of the general public sector. Different multilateral organizations can present extra grant financing and concessional lending, and risk-mitigating mechanisms will help develop their lending capability. Cooperation amongst multilateral establishments is important to align efforts and assets to attain a balanced allocation between mitigation and adaptation lending.
—This IMF weblog displays analysis by Cheng Hoon Lim, Ritu Basu, Yan Carriere-Swallow, Ken Kashiwase, Mahmut Kutlukaya, Mike Li, Ehraz Refayet, Dulani Seneviratne, Mouhamadou Sy, and Ruihua Yang.
IPS UN Bureau
© Inter Press Service (2024) — All Rights ReservedOriginal source: Inter Press Service




