
DOMINICA, Feb 12 (IPS) – The United Nations inaugural evaluation of the state of worldwide migratory species states that 1 in 5 faces extinction and warns that the world can’t afford to overlook this opportunity to behave on suggestions to guard, join, and restore habitats.A groundbreaking State of the World’s Migratory Species report is asking for accelerated international conservation measures to counter the specter of extinction confronted by 1 in 5 of all migratory species.
The report was launched on the opening press convention of the 14th Conference of Parties to the UN Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals (CMS COP14) in Samarkand, Uzbekistan, on Feb. 12.
It’s the first complete evaluation of migratory animals—species that journey to completely different components of the world yearly. They embody ocean species like sharks and sea turtles, terrestrial animals akin to elephants, in addition to these endeavor airborne journeys like birds and butterflies. The report’s authors say migratory species’ outstanding journeys not solely join the world; they provide a singular angle to analysis and perceive the magnitude of planetary adjustments.
The report has concluded that the conservation standing of migratory species general is deteriorating. Its outcomes have been described as “startling” by the Govt Secretary of the Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals (CMS), Amy Fraenkel.
“Overexploitation emerges as the best menace for a lot of migratory species, surpassing habitat loss and fragmentation,” she said within the report. “This contains the taking of species from the wild by intentional elimination, akin to by searching and fishing, in addition to the incidental seize of non-target species. Bycatch of non-target species in fisheries is a number one reason behind mortality of many CMS-listed marine species.”
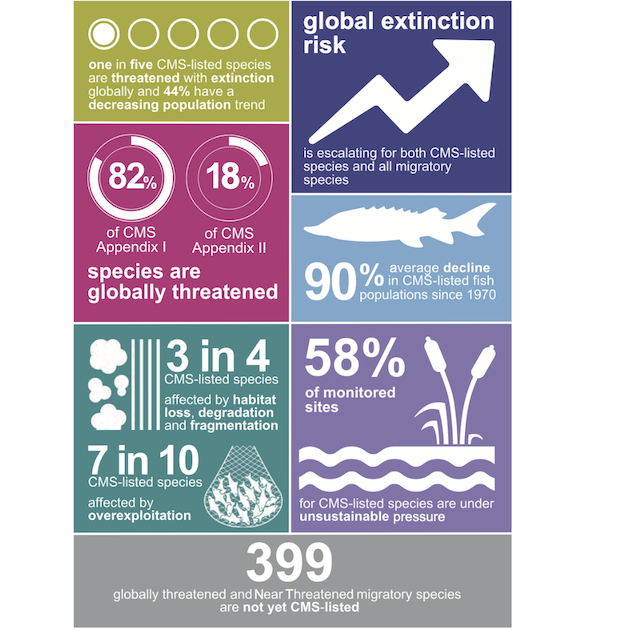
A few of the troubling findings embody inhabitants declines for nearly half of CMS migratory species, extinction threats for nearly all (97%) of CMS-listed fish, and a rising extinction threat for migratory species globally, together with these not listed below the CMS.
“Migratory species are of ecological, financial, and cultural significance. Inside ecosystems, they carry out quite a lot of essential features, starting from the large-scale switch of vitamins between environments to the optimistic impacts of grazing animals on grassland biodiversity,” the report states.
It provides that these species’ habitats and actions are in danger, with half experiencing unsustainable ranges of human-induced strain.
“The urgency for motion to guard and preserve these species turns into even higher once we think about the integral however undervalued function they play in sustaining the complicated ecosystems that assist a wholesome planet—by, for instance, transferring vitamins between environments, performing migratory grazing that helps the upkeep of carbon-storing habitats, and pollination and seed dispersal companies,” stated Inger Andersen, UN Below-Secretary-Normal and Govt Director, UN Setting Programme.
The current actuality for migratory species and the price of inaction or insufficient motion are regarding, however the report is heavy on each hope and concrete suggestions for international motion.
It accommodates a piece devoted to proposed coverage actions. Among the many most important are the necessity to tackle the unsustainable and unlawful harvesting of migratory species on the nationwide degree, measures to cut back bycatch and different incidental captures, and the identification and recognition of all vital websites for migratory species.
The suggestions are to “defend, join, and restore” habitats, deal with overexploitation, cut back the damaging impacts of environmental air pollution, tackle the foundation causes and cross-cutting impacts of local weather change, and make sure the CMS Appendices defend all migratory species in want of additional conservation motion. In addition they name for ‘follow-through’ on international commitments to ecosystem restoration.
“This contains these linked to the UN Decade on Ecosystem Restoration and Goal 2 of the Kunming-Montreal World Biodiversity Framework to make sure that at the least 30% of degraded terrestrial, inland water, and coastal and marine ecosystems are below efficient restoration by 2030. To assist these efforts, develop and implement nationwide restoration plans centered on restoring and sustaining necessary habitats for migratory species,” it states.
UNEP’s Inger Andersen says the report is a vital milestone within the institution of a roadmap for the conservation of migratory species.
“Given the precarious scenario of many of those animals and their important function for wholesome and well-functioning ecosystems, we should not miss this opportunity to behave—beginning now by urgently implementing the suggestions set out on this report,” she said.
For the CMS’ Amy Fraenkel, conservation of migratory species is a shared accountability among the many world’s nations.
“Migratory species are a shared pure treasure. This landmark report will assist underpin much-needed coverage actions to make sure that they proceed to traverse the world’s skies, lands, oceans, lakes, and rivers.”
IPS UN Bureau Report
Follow @IPSNewsUNBureau
Follow IPS News UN Bureau on Instagram
© Inter Press Service (2024) — All Rights ReservedOriginal source: Inter Press Service





